Companhia Águas de Joinville (CAJ), State of Santa Catarina, Brazil
WGIC Secretariat
on
February 27, 2024
Aerial picture of Joinville, Brazil
- WGIC partner(s): Bentley Systems
- City journey step(s): Implement; Develop Actions and Adaptation Strategy
- Geospatial data type(s): Risks, vulnerabilities and resource management; Digital twins and modeling
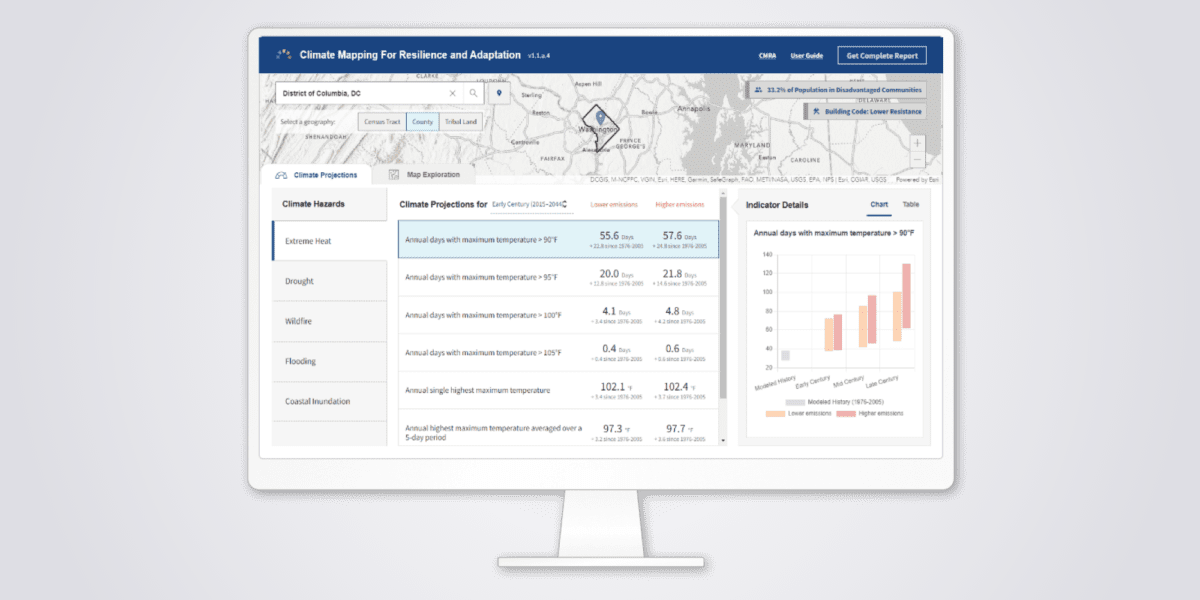
After a severe water crisis, the city of Joinville developed a contingency plan to maintain water supply during drought conditions. Preliminary simulations produced water shortages, so the city sought a more comprehensive network study and used Bentley applications to create a digital twin and perform a hydraulic analysis of the distribution system. The new contingency plan redistributed water across two sources – Cubatão and Piraí – guaranteeing water supply during severe drought and improving overall water distribution to the city. The proposed solution required less capital investment for implementation because it could optimize flow between city sectors utilizing the existing network and remove the need for costly additional piping and pumping (saving BRL 4.5M). The solution reduced production by 30%, equivalent to 170 liters per second in the fragile Piraí water source. This mitigated the effects of drought, benefiting 150,000 area residents. It also resolved issues within the Cubatão system, reducing water loss in critical district metered areas by 40,000 cubic meters per month and water shortage complaints by 90%.